When you make purchases via these links, Business Insider might receive an affiliate commission.
Learn more
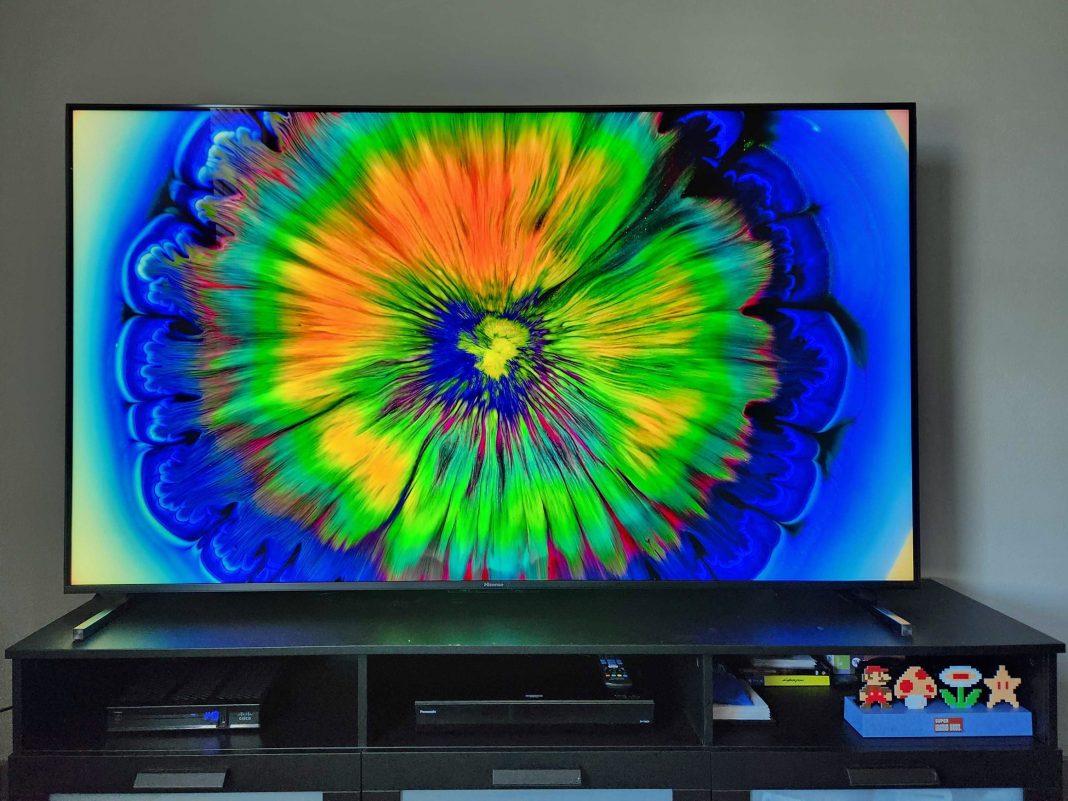
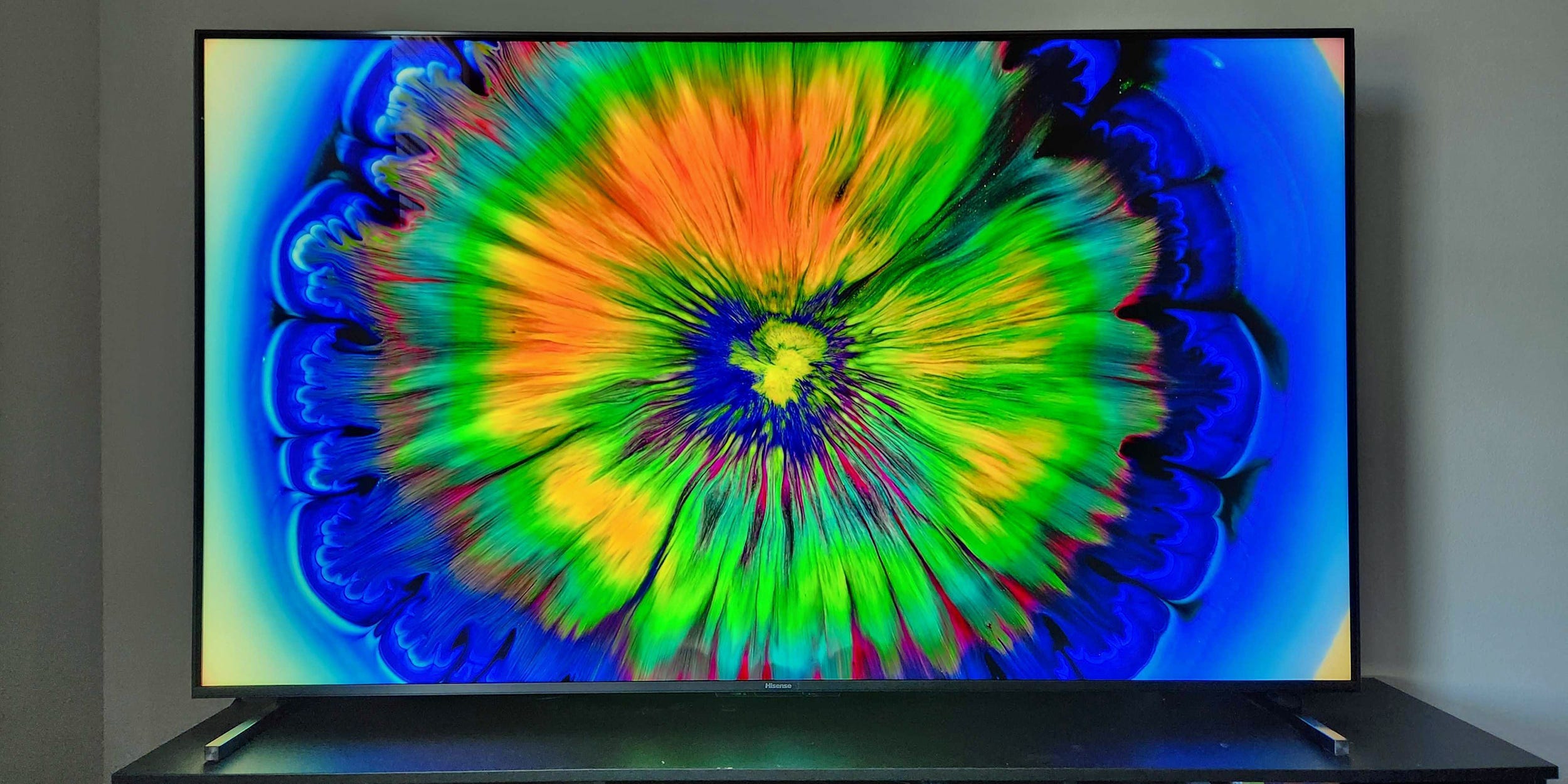
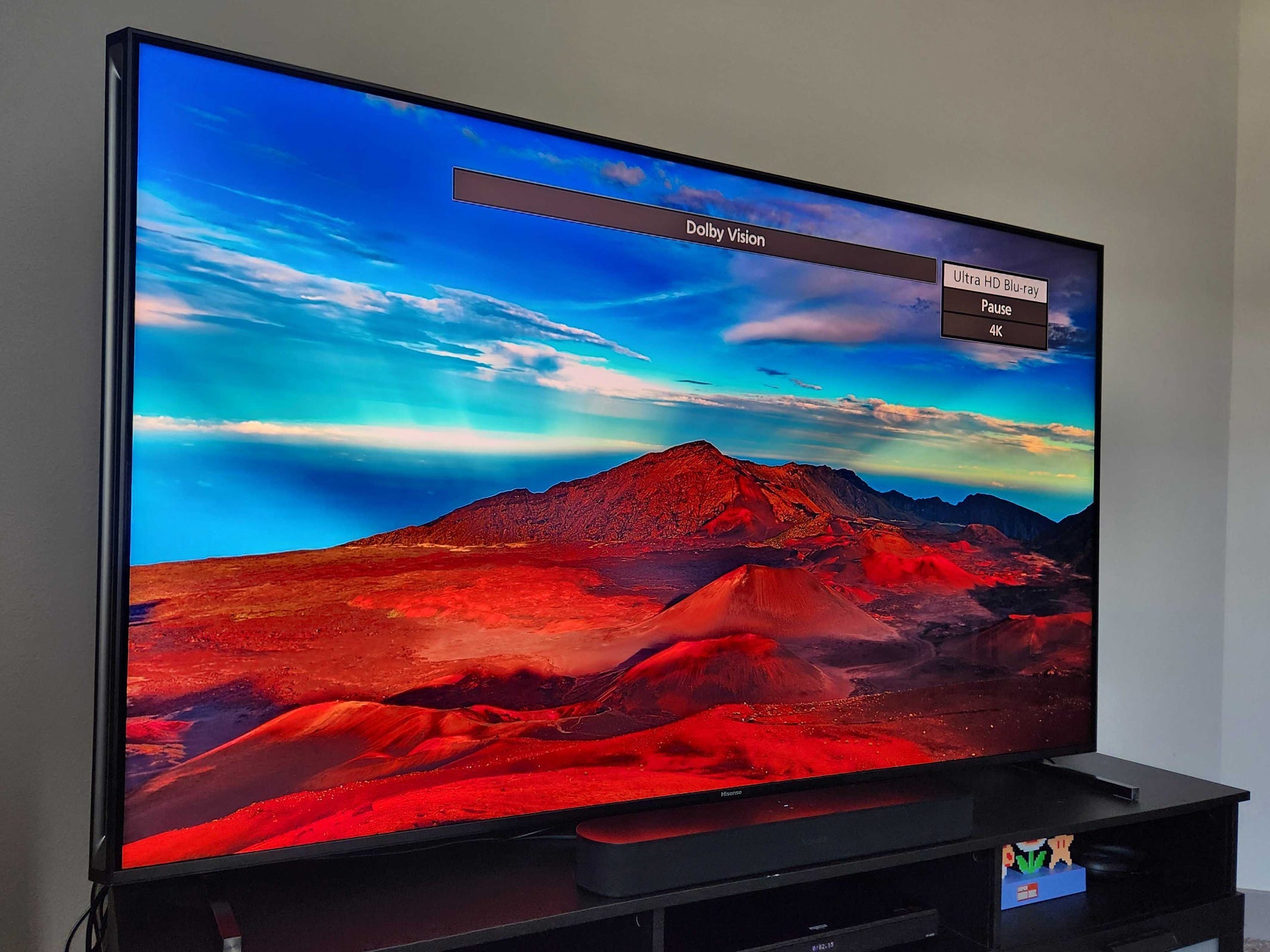
High Dynamic Range (HDR), a technology included in numerous contemporary televisions, significantly improves image quality. This capability enables screens to show pictures with greater luminosity levels, superior contrast ratios, and an extended color spectrum. Essentially, HDR makes visuals stand out vividly, seem more lifelike, and align closely with what their producers envisioned.
However, while HDR has become a standard feature on numerous devices nowadays,
best TVs
, performance can vary significantly between different models. Simply stating that a display supports HDR does not guarantee it will effectively utilize this feature. For instance, some affordable options, such as certain budget-friendly sets, may struggle to deliver optimal HDR visuals.
Roku Plus Series
It does a good job providing basic level HDR performance, however, for an outstanding HDR experience, you should consider getting a high-end OLED display, such as the
Samsung S95F
, or a vibrant QLED TV featuring Mini LEDs, such as the
TCL QM7
.
To assist with navigating the intricacies of high dynamic range technology, we have compiled an extensive guide outlining all the essential information regarding HDR televisions and various formats.
What does HDR stand for in televisions?
High Dynamic Range (HDR) is a display technology designed to enhance the contrast capabilities of TVs and monitors when they play HDR-encoded content. It ensures that brightly lit parts appear even brighter and shadowy areas remain deeply dark, thereby maintaining greater detail across every gradation from light to dark within images.
HDR enhances visual depth by revealing finer details and offering greater realism in bright reflections and dark areas. Consider a scenario where sunlight sparkles across the sea. In the absence of HDR, such a scene might appear flat with diminished clarity and overexposed spots. However, thanks to HDR’s wider dynamic range, these intense highlights have space to stand out vividly. This makes the reflected light both brighter and richer in texture at the same time.
The brightness of HDR content is quantified using units known as nits. A display’s capacity to generate higher numbers of nits correlates directly with how vividly bright the highlights appear within an image. Typically, most HDR movies and television programs are created considering a peak nit value ranging from approximately 1,000 to 4,000; however, theoretically, they could reach up to 10,000 nits. Nonetheless, only a small fraction of household screens manage to attain this extreme level. High-end HDR televisions usually top off at between 1,500 to 4,000 nits, whereas mid-tier versions generally provide somewhere in the range of 700 to 1,500 nits. Entry-level alternatives typically deliver about 400 to 700 nits.
What does Wide Color Gamut refer to?
High Dynamic Range (HDR) frequently comes paired with another display characteristic known as Wide Color Gamut (WCG). This allows a television to show a broader spectrum of colors. Although these are distinct technologies, videos mastered in HDR typically utilize a wide color gamut, making WCG commonly regarded as an integral aspect of HDR technology.
When using WCG, HDR videos are encoded within a color space called Rec. 2020, though most HDR movies and TV shows are actually graded for a narrower standard called DCI-P3. DCI-P3 is the same range of colors used for modern digital theater projection, while Rec. 2020 can offer an even wider range than that.
So, with HDR and WCG, you can enjoy the full spectrum of colors you see in theaters at home.
How does HDR compare to SDR?
Before the first consumer HDR displays hit the market in 2015, TVs were built to adhere to a standard dynamic range (SDR) specification. SDR displays and content are designed with a max of only 100 nits in mind, and they’re typically produced for a limited color gamut called Rec. 709. Compared to the DCI-P3 color space used on most HDR videos, Rec. 709 offers a more restricted gamut of colors.
This means that SDR displays produce comparatively dim and low-contrast images with a narrower range of colors when compared to an HDR TV playing HDR programming. As a result, an SDR version of a movie or TV show will often look a bit flat and muted compared to its HDR counterpart.
Although not as prevalent today, high-definition and 4K-resolution SDR televisions continue to be produced, and all HDR-capable sets remain able to accurately show SDR signals. Despite HDR mastering being increasingly favored for new on-demand streaming services and 4K Blu-ray releases, SDR remains standard for cable and satellite broadcasts.
live TV streaming
, and
over-the-air broadcasts
.
What steps should I follow to view HDR movies and television programs?
To enjoy HDR videos, you require both an HDR-compatible screen and HDR-encoded material. Additionally, every device in your home entertainment setup must support HDR. This means that if you use a streaming device, it should be HDR capable. If your media player connects to your television via an AV receiver or soundbar, these accessories too must have HDR pass-through capability. Furthermore, ensure all gadgets are connected with either premium or ultra-high-speed HDMI cables. For more details, refer to our guide on this topic.
best HDMI cables
for recommendations.
HDR videos are available on all the
best streaming services
, including Disney Plus, Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video. HDR is also used on most 4K Ultra HD Blu-ray discs. Some live sporting events are also shown in HDR through certain providers, but the vast majority of cable, satellite, and livestreaming broadcasts are still presented in SDR.
What should I look for in an HDR TV?
All of the
best 4K TVs
include some level of HDR support, and some HDTVs even have HDR capabilities. However, performance varies dramatically between cheaper models and more expensive displays.
For optimal HDR performance, consider purchasing either an OLED TV or a QLED display equipped with local dimming and extended color range. Certain high-end QLED models are also referred to as Mini LED TVs because they utilize smaller LEDs for their backlighting, which allows for better control over brightness levels.
All these display options provide the contrast adjustment, maximum luminance, and color features required to effectively demonstrate the advantages of HDR content. To learn about the distinctions between OLED and QLED televisions, refer to our guide.
QLED vs. OLED
comparison.
If you’re aiming for impressive HDR quality, prioritize selecting a display capable of producing at least 1,000 nits or more when it comes to brightness levels. Nevertheless, screens offering this degree of performance usually come with a heftier price tag; nonetheless, budget-friendly options providing decent entry-level HDR can achieve up to around 500 to 600 nits.
Several high-end HDR TVs currently on the market include the
LG G5 OLED
,
Samsung S95F OLED
,
Sony Bravia 9 QLED
, and
Hisense U9N QLED
. Mid-range choices encompass models such as the
Samsung S90D OLED
,
LG C4 OLED
, and
TCL QM7 QLED
. Meanwhile, the
Hisense U6N QLED
and
Roku Plus Series QLED
They are both excellent choices for those looking at cost-effective options.
To find additional suggestions, explore our different television buyer’s guides:
- Best budget TVs
- Best TVs under $500
- Best smart TVs
- Best OLED TVs
- Best 100-inch TVs
- Best 85-inch TVs
- Best 75-inch TVs
- Best 65-inch TVs
- Best 55-inch TVs
- Best 50-inch TVs
Are there different HDR formats?
Certainly, there are four main HDR video formats:
HDR10
,
HDR10+
,
Dolby Vision
, and
HLG
.
HDR10
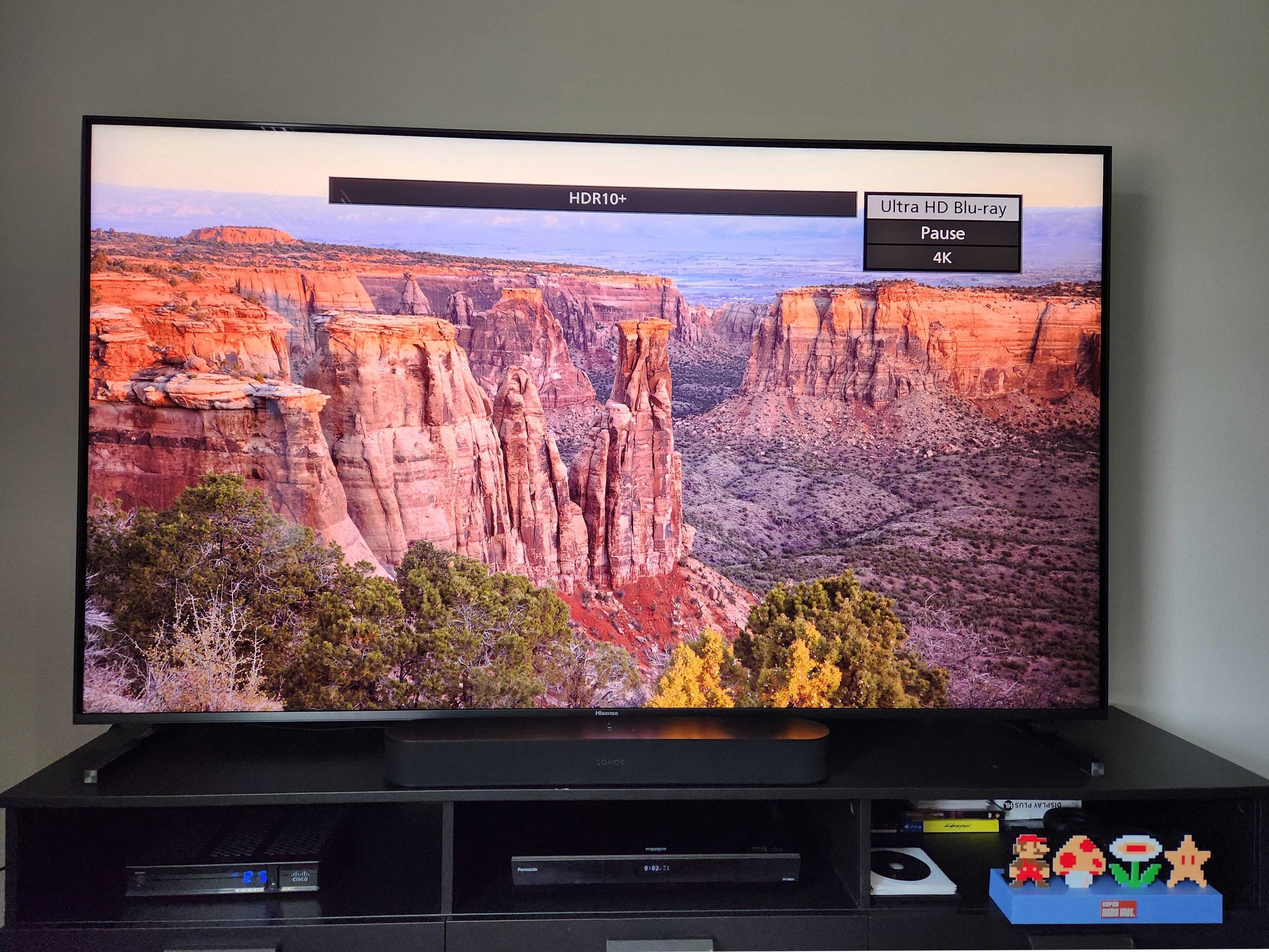
It stands as the simplest and most widespread HDR format. This format is compatible with every HDR television and serves as the standard for HDR on all 4K Ultra HD Blu-ray discs and streaming services offering HDR content. Essentially, you could say it acts as the foundational HDR stratum upon which more sophisticated HDR formats can be layered.
HDR10 videos have the potential to reach peaks of brightness up to 10,000 nits when mastering; nonetheless, most HDR10 content typically ranges from 1,000 to 4,000 nits. These videos include static metadata which instructs TVs on color representation and desired image luminosity levels. Yet, this static metadata approach is somewhat restricted because it applies uniform settings across an entire video rather than adjusting individually per scene.
When you play an HDR10 movie on an HDR television that lacks the ability to fully reproduce the wide range of brightness and colors specified in the video’s metadata, the screen needs to adjust autonomously. It scales back highlight details and color intensity so they fit within what the display can manage. This process is referred to as “tone mapping,” and various brands implement this technique uniquely based on their technology.
In reality, this can result in problems with specific scenes in HDR10 videos looking either overly bright or excessively dark because a television’s tone mapping might not align with what the content creator envisioned. This discrepancy is precisely where the issue arises.
Dolby Vision
and
HDR10+
come in.
Both Dolby Vision and HDR10+ use “dynamic metadata” for high dynamic range imaging, which allows them to specify details about brightness and colors on a per-scene or individual frame level. Consequently, these advanced formats offer more precise guidance to televisions regarding tonal adjustments, ensuring that content appears as originally intended by the creators. You’ll find support for these technologies in specific models of smart TVs, Blu-ray discs, and various online platforms.
Finally,
HLG
HDR format is utilized in TV broadcasts. Unlike others, this particular format doesn’t employ metadata whatsoever and maintains compatibility with SDR displays. Consequently, content providers can transmit an HLG signal universally; viewers will see accurate imagery whether they own HDR or SDR televisions. Transmitting another type of HDR broadcast to an SDR television set could result in incorrect color representation and poor contrast adjustment.
Are Dolby Vision and HDR10+ better than HDR10?
Indeed, HDR10+ and Dolby Vision can provide a more precise high-dynamic-range image compared to the basic HDR10 format. Nonetheless, these enhancements tend to be nuanced and are typically noticed most clearly on less expensive and moderately priced HDR televisions. These sets stand to gain significantly from the advanced dynamic tone-mapping directives of HDR10+ and Dolby Vision.
Common HDR television models usually provide compatibility with either or both of these dynamic metadata standards. However, generally speaking, we do not consider it crucial whether one format is supported and the other is not.
Is Dolby Vision superior to HDR10+?
Dolby Vision and HDR10+ provide similar main advantages when compared to HDR10, with each format not having a significant technical superiority over the other. Nonetheless, Dolby Vision has usually held an upper hand regarding industry backing. Still, it’s worth noting that support for HDR10+ has been growing steadily.
Out of the seven prominent television manufacturers in the U.S., six offer televisions equipped with Dolby Vision capability, whereas five of these same companies provide models supporting HDR10+. Below is a table outlining which TV brands have sets featuring both Dolby Vision and HDR10+ technology.
| Brand | Dolby Vision | HDR10+ | HDR10 |
| Hisense | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| LG | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Panasonic | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Samsung | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Sony | ✓ | ✓ | |
| TCL | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Vizio | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
In terms of content availability, Dolby Vision movies and television series are more common than those using HDR10+. A greater number of studios back Dolby Vision for Ultra HD Blu-ray releases, and many streaming providers utilize this technology. Nevertheless, some platforms such as Netflix and Disney Plus have recently disclosed their plans to introduce HDR10+ compatibility soon. Below is an overview of how various leading streaming services handle Dolby Vision and HDR10+.
| Streaming service | Dolby Vision | HDR10+ | HDR10 |
| Amazon Prime Video | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Apple TV Plus | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Disney Plus* | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Max | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Hulu | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Paramount Plus | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Peacock | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Netflix | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
*Disney Plus has revealed its intentions to introduce HDR10+ support before the end of this year.
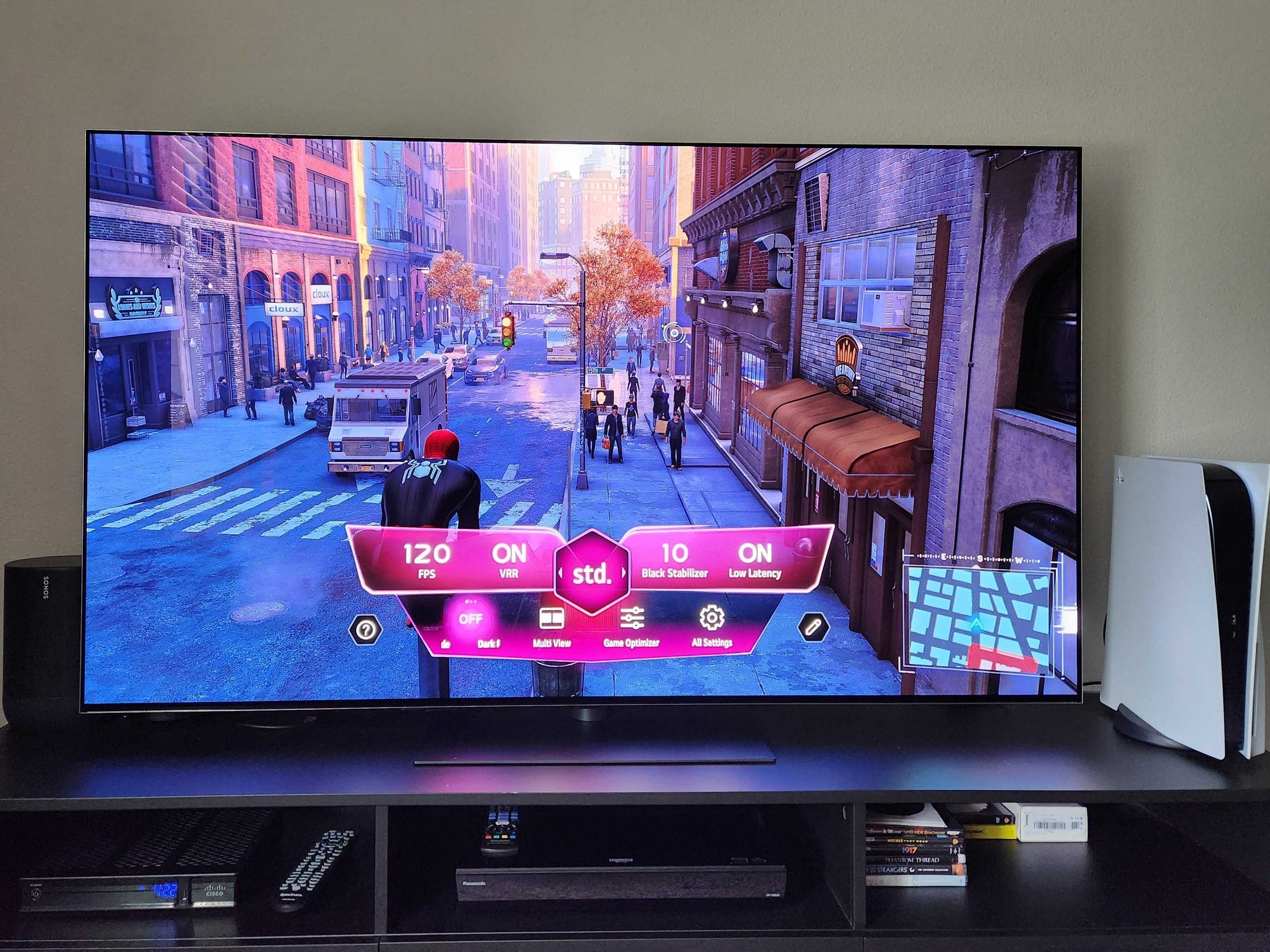
Can video games utilize HDR technology?
High Dynamic Range (HDR) gaming is supported on PS4, PS4 Pro, PS5, Xbox One X/S, Xbox Series X, Xbox Series S, as well as on compatible PCs. Nonetheless, not all titles come equipped with built-in HDR functionality.
Windows PCs have the capability to run games with HDR10, HDR10+, and Dolby Vision formatting. Both the Xbox Series X and Xbox Series S models support HDR10 along with Dolby Vision technology. In contrast, the PS5 supports only HDR10 format for gaming.
If you’re utilizing a PC, ensure your operating system, monitor, and graphics card all accommodate HDR for the proper depiction of HDR games.
The Nintendo Switch lacks HDR support; however, the newer model
Nintendo Switch 2
Will support HDR10 gaming both in handheld and docked modes upon its release in June.
If you liked this tale, make sure to follow
Business Insider
on MSN.